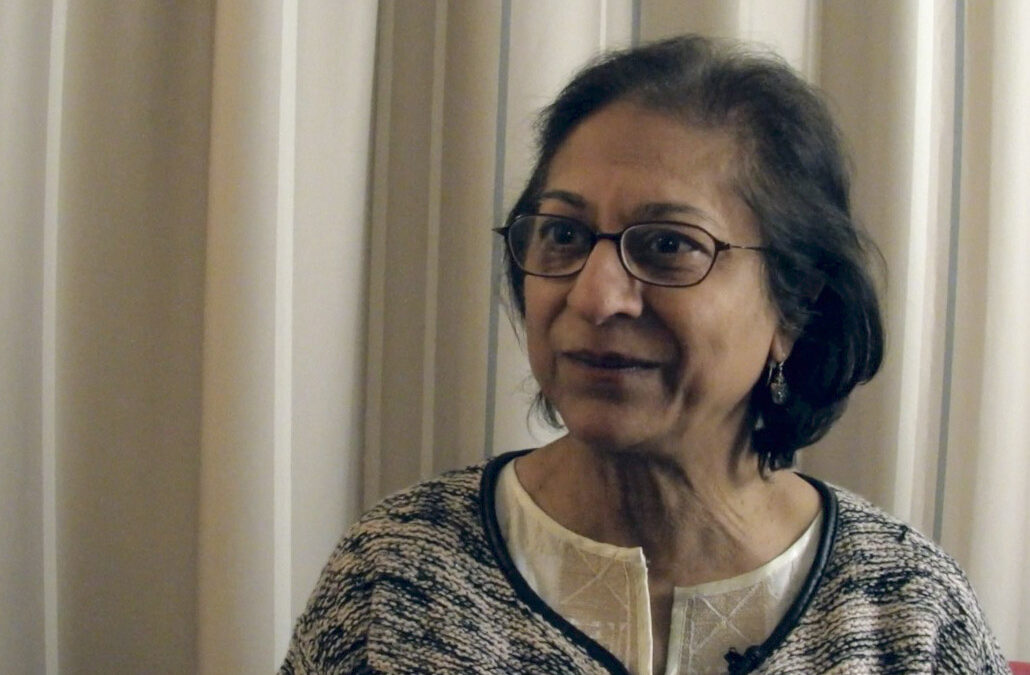
Apr 28, 2017 | Multimedia items, News, Video clips
Honorary Member of the ICJ, Asma Jahangir, talks of her experiences as part of the ICJ’s ongoing profile series on women human rights defenders.
Asma Jahangir became interested in human rights legal work after having witnessed the frequent arrests of her father, an outspoken critic of military dictatorships, and seeing the courtroom as a place where justice could be accessed. From these early experiences, Asma identified the importance of rule of law but came to understand that this was something that went far beyond the courtrooms of Pakistan.
As a married women, her in-laws had concerns about her practicing law in a mixed firm so she co-founded Pakistan’s first all-female law firm. Initially the firm was viewed as a hobby but Asma and her other co-founders persevered and the firm still thrives today.
Ms Jahangir spoke about the challenges she faced as a female lawyer where courts and judges were at first patronizing towards her and then became angry at her as she continued to present them with cases that were challenging for them. She worked on a number of landmark cases including about whether women could get married without their fathers’ permission, be entitled to family maintenance and whether women should be judged according to religious or codified law.
Women in Pakistan face many issues in accessing justice, Ms Jahangir said. They lack resources, if they are able to access the courts they are frequently exploited by male lawyers and they encounter prejudice in their cases. In addition many laws are simply discriminatory, however women have been challenging these and will continue to do so.
There has been progress in family law in Pakistan, particularly in relation to the procedures if not the substance, yet Pakistan remains a long way from having equality in the family law framework.
Asma noted that it can be hard to engage men in women’s rights issues but commented that many men who had not considered giving certain rights to their wives had become a lot more conscious about women’s rights issues as their daughters had grown up. Many of her colleagues now ask for internships for their daughters at her law firm and admit how narrow-minded they had previously been in relation to women’s rights and equality.
From 2004 to 2010, Ms Jahangir served as the UN Special Rapporteur on Freedom of Religion and explained that she worked with the Special Rapporteur on Freedom of Expression to address the delicate balance in managing freedom of religion and freedom of expression.
Freedom of expression is currently under threat around the world, Asma commented, and is being undermined in the name of a variety of reasons including security, religion and tradition or social norms. Asma said that freedom of expression is fundamental to basic human rights because stopping freedom of expression stops people from thinking.
“Self-censorship is a by-product of undermining freedom of expression and self-censorship by itself dis-informs people, brings out irrelevant issues, and suppresses the more relevant issues.”
Ms Jahangir told the ICJ that in the course of her work as a human rights activist she has been threatened, put under house arrest and imprisoned. However, rather than deterring her, Asma’s experience in jail made her stronger: “It made every woman who went to jail stronger and more resolute that we want rights.”
There was a particular case that had a strong impact on Asma, which was when she worked in defence of a child who had been accused of blasphemy and was sentenced to death. The initial verdict against the boy knocked her confidence as a lawyer, but senior colleagues encouraged her and she continued with the case, taking this to appeal.
This was a very contentious case that attracted a lot of negative attention against Ms Jahanagir. People claimed she was anti-Muslim and, as she argued for the defendant, crowds gathered outside the court calling for her execution. At one point opposing lawyers asked the judges if they could simply close the case but the judges said that if Asma was prepared to keep arguing they were prepared to hear her arguments.
Asma explained that she was inspired to continue by the defendant himself, a boy of around 14 years of age, who, when given the opportunity to run away whilst on bail, decided to stay and continue the trial rather than risk others being harmed in retaliation if he were to flee. She felt that even if she had to give her life to defend this child then it would be worth it. Ultimately the case was decided in the boy’s favour and he was acquitted.
She advised young women interested in a career as a human rights lawyer not to label themselves as ‘human rights lawyers’ rather than simply ‘lawyers’ or they will not be taken seriously. Asma said that “I think that life where you don’t have dignity and where you don’t fight for people’s dignity is a wasted life.”
Watch the interview:
The series of profiles introducing the work of ICJ Commissioners and Honorary Members on women’s rights was launched on 25 November 2016 to coincide with the International Day to Eliminate Violence against Women and the first day of the 16 Days of Activism Against Gender-Based Violence Campaign.

Mar 27, 2017 | Multimedia items, News, Video clips
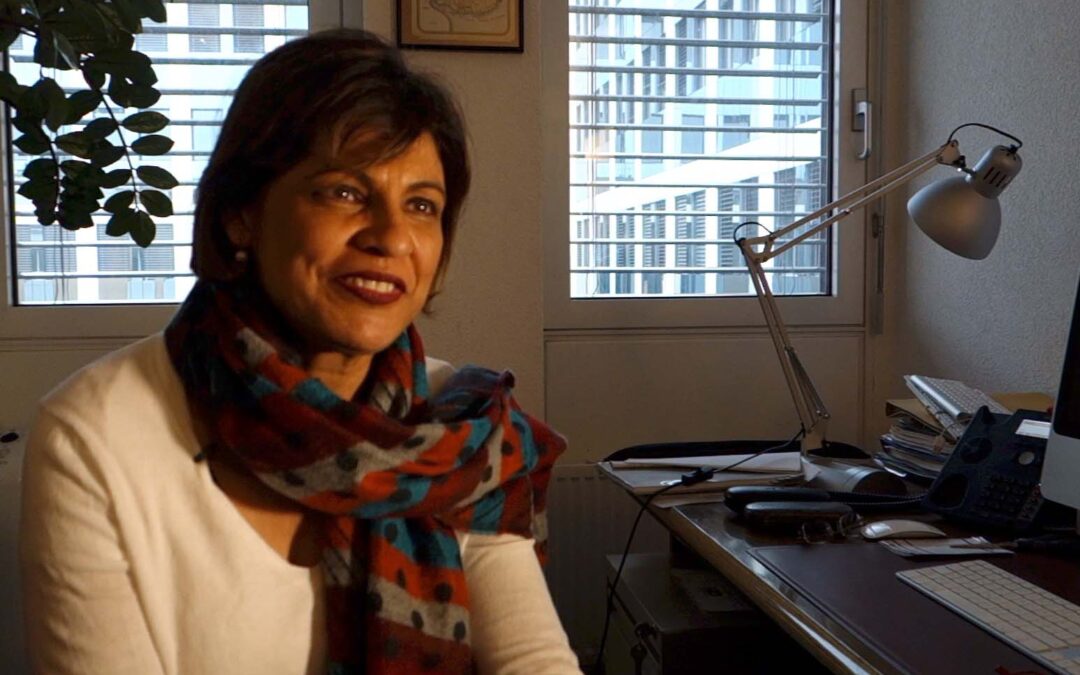
The ICJ continues its series of women’s rights defender profiles with an interview with Imrana Jalal, an ICJ Executive Committee member, focussing on her motivations for women’s rights work.

Feb 27, 2017 | Multimedia items, News, Video clips
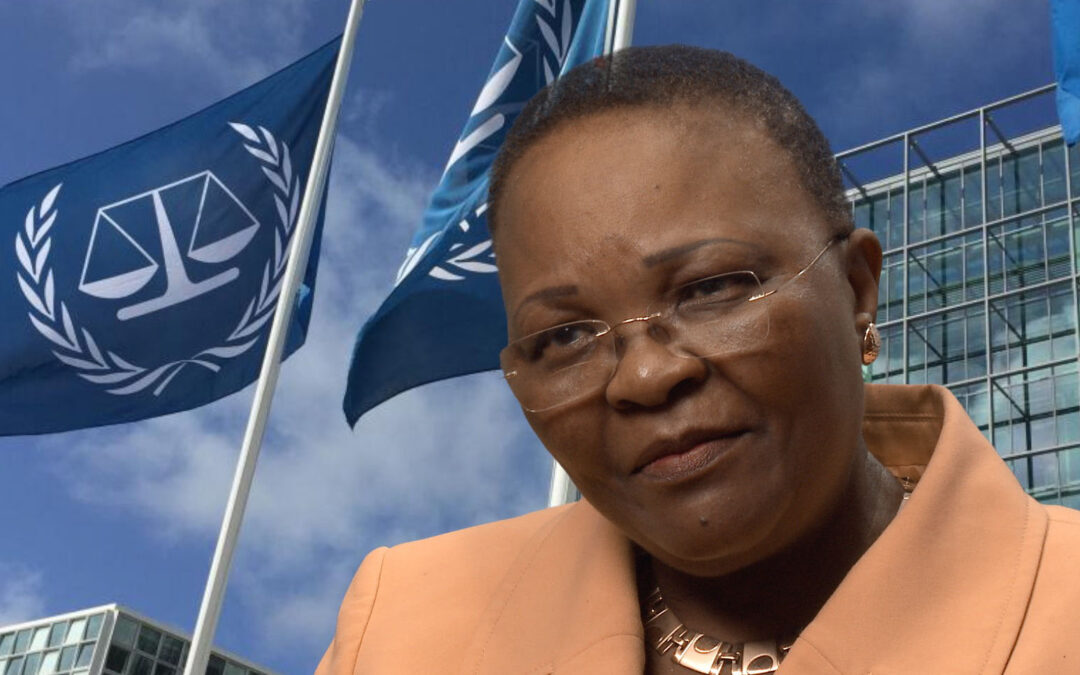
The ICJ continues it’s monthly profile series on women’s rights defenders with an interview with ICJ Commissioner and International Criminal Court Justice Sanji Monageng.
Justice Monageng told the ICJ that her interest in women’s rights began when she went through her own divorce and encountered the injustices that Botswana women suffered. This motivated her to pursue a career in law and align herself with the women’s rights movement that was establishing itself in southern Africa.
She became the Founder and Chief Executive of the Law Society in Botswana, a Magistrate in Botswana and High Court Judge in the Gambia and Swaziland. She was elected a Commissioner of the African Commission on Human and Peoples’ Rights and served as Chair of the Commission. She has been a Judge of the International Criminal Court since 2009 and served as First Vice-President between 2012-2015.
Justice Monageng commented that in Botswana, and elsewhere in southern Africa, women were at a serious disadvantage when it came to access to justice because of cultural, customary and religious restraints as well as economic inequality.
For example, up until only a few years ago women in Botswana were unable to inherit their parent’s property, on the basis of customary law, but a progressive judge was not afraid to challenge this and when this judgement was supported this led to a real change in the lives of women.
Sanji spoke of the importance of a strong civil rights movement and noted how instrumental this had been in Africa in leading the agenda to promote progressive rights protection for women. The African Commission on Human and Peoples’ Rights has a Special Rapporteur on Women and the Protocol to the African Charter on Human and Peoples Rights on the Rights of Women in Africa (the Maputo Protocol) has been hailed as the best in the world.
At the International Criminal Court (the ICC) there is a coalition of some 2,500 NGOs that work very closely with the court and have been instrumental in driving key aspects of the Court’s work including addressing sexual violence and ensuring victim and women’s participation. ‘Without civil society, without NGOs, and we have witnessed very credible civil society organisations’, Sanji says, ‘we cannot move.’
However, Justice Monageng commented that the ICC has not done very well in prosecuting sexual and gender based violence so far but acknowledges that the Court is still young and that progress is being made.
The new Chief Prosecutor, Fatou Bensouda, has undertaken a lot of endeavours to promote this aspect of the Court’s mandate such as creating a policy on sexual violence and gender issues, establishing a dedicated unit to address these crimes and appointing the highly qualified Brigid Inder as her Special Gender Advisor. Sanji commented that it is now evident in the cases she sees as a judge that a lot more attention is being paid to sexual violence.
Justice Monageng suggests that young women interested in defending women’s rights must internalize the importance of human rights. They should start associating themselves with women’s rights organizations even if only in a small way.
Defending women’s rights is difficult work and those that are interested in this must be prepared for criticism, and other unpleasantness but this work needs to be done. ‘The world is upside down and human rights are forgotten in most instances’, Sanji says, so she looks forward to girls joining the women’s rights movement.
Watch the interview:
The series of profiles introducing the work of ICJ Commissioners and Honorary Members on women’s rights was launched on 25 November 2016 to coincide with the International Day to Eliminate Violence against Women and the first day of the 16 Days of Activism Against Gender-Based Violence Campaign.

Jan 31, 2017 | Multimedia items, News, Video clips
The ICJ continues its series of profiles of ICJ’s women Commissioners with an interview with ICJ Vice-President Michèle Rivet.
Michèle Rivet was a judge for 30 years. Previously a Children’s Judge, she was appointed the first President of the Quebec Human Rights Tribunal when it was first established in 1990 and remained in that position until 2010.
In the interview she explains how the Human Rights Tribunal was constituted and how the Tribunal gave itself the mission to develop jurisprudence on equality and non-discrimination by referring to the fundamental international standards elaborated in the ICCPR and the ICESCR, by giving them the broadest interpretation possible.
A key goal of the Tribunal was to ensure that it was as accessible and as effective as possible, so that the people who came to the Tribunal could express themselves freely. Careful measures were taken to ensure that the Tribunal would work well and to ensure that anyone putting questions or issues to the Tribunal could know that the judges were listening to them and would provide an answer.
Michèle spoke of the advances that were achieved in the Tribunal. Some of the most significant decisions handed down by the Tribunal refer to cases of multi-faceted systemic discrimination. Justice Rivet explained that discrimination is about daily life: for example it may be a woman who is fired because she is pregnant, or it could be about a homosexual person who is refused accommodation.
A particular case referred to a large Canadian gas company, a big employer in Quebec, where women were never being appointed to certain posts, as there were a whole series of barriers at the point of recruitment, at the level of tests, and other conditions. After a series of profound reflections, evidence gathering and a long hearing the Tribunal reached the decision that the five women plaintiffs had been discriminated against.
However, the Tribunal also went further in its judgement by requesting that an equal access employment programme be implemented for the whole staff. The Court of Appeal upheld the decision on appeal and that decision marked a real victory for women in the recognition of their rights.
Michèle considers that the ICJ, with its mandate to promote the rule of law, acts as a laboratory of great ideas and carries out fundamental and far-reaching work to advance the rights for those who otherwise would not be able to speak.
Those who work in the field of human rights form a global village, said Michèle, and members have a duty to help women victims of violence: those forced to marry when they are 13 years old, those forced to keep their children because abortion is not an option and all those who are battered or disfigured by relatives because they dare to leave the home.
“This eventually led to the establishment of an international community of women and of all those who are fighting for equality, and for a society where everyone is fully integrated,” she said.
Justice Rivet considers herself privileged to work in the field of human rights as it is such rewarding work, and although it can be also be very challenging she says “we must all walk together on the long march towards equality.”
Watch the interview:
The series of profiles introducing the work of ICJ Commissioners and Honorary Members on women’s rights was launched on 25 November 2016 to coincide with the International Day to Eliminate Violence against Women and the first day of the 16 Days of Activism Against Gender-Based Violence Campaign.

Dec 20, 2016 | Multimedia items, News, Video clips
The ICJ continues its profile series of women’s rights defenders with ICJ Commissioner Hina Jilani.
Hina Jilani is a human rights activist and an advocate of the Supreme Court of Pakistan, she has served as the first UN Special Representative on Human Rights Defenders to the Secretary-General and has been an ICJ Commissioner since 2013. In 1980, Hina co-founded Pakistan’s first all-female legal aid practice, AGHS Legal Aid Cell (ALAC).
Hina started her legal career at a time of an oppressive military government takeover in Pakistan. The government sought to legitimize their authority on the basis of Islam, which they interpreted as meaning lesser rights for women who were reduced to second-class citizens and denied the same rights as men. This sparked Hina’s passionate commitment to women’s rights work.
The women’s rights movement in Pakistan has declared itself a secular movement, having decided that it is better to separate the question of religion and universal rights. Hina said that Islam doesn’t deny rights to anyone but that when it is used by those in positions of authority they can interpret religion in ways that suit their own political needs and this results in inequality.
Domestic violence is a major problem in Pakistan and Hina said that most women will have experienced this in one form or another at some point in their lives.
Hina identified a lack of social mobility and social prejudices as key challenges that women in Pakistan face in accessing justice.
In a society where women are encouraged to stay at home many women are unable to access the legal and other services they may need if their rights are being abused. Many women do not even have an awareness of what their rights are, nor do they have access to information about their rights or the kinds of people that could provide them with this information.
In addition, where women do seek justice through the legal system they often encounter social prejudices from those administering that system.
However, although the Pakistani judiciary has traditionally been very conservative there has been a lot of progress in this area. Ms Jilani thinks this is a results of women’s rights advocates taking cases to courts and presenting these in a way that makes the social inequalities and injustices apparent and makes it easier for judges to make better decision that challenge these prejudices.
Ms Jilani recommends three steps for eradicating violence against women:
Firstly, it is essential to have strong legislation; having something anchored in the law makes it incumbent for authorities and institutions to provide women with protection and justice.
Secondly, there must be mechanisms on the ground that make it possible for women to assert their rights under any such legislation; this goes beyond legal support and will include cross-sectoral services such as women’s shelters.
Thirdly, there must be independent judges administering the legislation; judges must be independent not only of the executive but also of their own social prejudices.
Defending women’s rights in the courts of law has seen some significant victories in terms of clarifying the whole meaning of equality and equal opportunity. However, Hina said that the most difficult rights protection work women can do is defending women’s rights.
Women’s rights defenders “are seen as change-makers who are not necessarily liked so they are targeted”. They are often vulnerable to exclusion, social isolation and being discredited, both within their wider communities and also, often, within their own families.
Hina Jilani recommends that women who engage in rights defence work develop strong support networks that also makes link with other rights movements. The more it is apparent they are not acting in isolation, the better protected they will be.
Watch the interview:
The series of profiles introducing the work of ICJ Commissioners and Honorary Members on women’s rights was launched on 25 November 2016 to coincide with the International Day to Eliminate Violence against Women and the first day of the 16 Days of Activism Against Gender-Based Violence Campaign.

Nov 25, 2016 | Multimedia items, News, Video clips
The ICJ has launched a new women’s rights defenders profile series, beginning with ICJ Commissioner and Justice of the Supreme Court of Serbia, Radmila Dragicevic-Dicic.
The monthly profile series, introducing the work of ICJ Commissioners and Honorary Members on women’s rights, has been launched to coincide with the International Day to Eliminate Violence against Women and the first day of the 16 Days of Activism Against Gender-Based Violence Campaign.
The Judges Association of Serbia was established by Radmila and others in 1997, during the regime of Slobodan Milosevic. The Association was formed under the slogan ‘I do not agree’ in opposition to the misuse of the judiciary. Many women were involved in this fight against corruption and in protection of the independence of the judiciary.
In the year 2000, shortly before the fall of Milosevic, Radmila was one of fifteen judges that were dismissed because of their opposition to the repressive regime; although she was quickly reinstated following the elections that took place later that year.
During the civil war period in the 1990s, violence against women grew significantly and domestic violence was rampant in Serbia. Radmila, and other women in the judiciary, worked on issues of organized crime and human trafficking and they were brave to do so as the State couldn’t guarantee their security.
Radmila spoke of women’s continued obstacles in accessing justice and the important of protecting victims of violence. She commented that some States still lack the facilities, resources, personnel and awareness to provide adequate protection for victims.
Human trafficking continues to be one of the biggest problems that affects women, not only in Europe but globally. Justice Dragicevic-Dicic said it was beneficial for those working on women’s rights to share their experiences and learn from one another. Although the motivations and circumstances of women trafficked in different parts of the world may vary, all these women are subject to the same kinds of violence.
In the Serbian constitution, human trafficking is categorized as a crime against humanity and is taken very seriously, although this was not always the case.
Radmila spoke of one case she presided over that helped her to understand what it meant to be a victim. The case concerned two Ukrainian students who had dreamt of going to work in Germany to earn some money for their families but were trafficked into prostitution. She said that this case helped her to understand that anyone can be a victim.
It is everyone’s right to have dreams and to be naïve but no-one has the right to violate your rights. Radmila works to raise awareness amongst other judges that their role is not to judge the victims but those that have exploited them.
There remains a number of issues for victims of trafficking that Justice Dragicevic-Dicic highlighted, including ensuring the non-punishment, safety and protection of victims as well as addressing their access to compensation. Even where the offender isn’t known, victims are still entitled to the full rights of a victim within criminal proceedings.
The judiciary and independent organizations, like the Association of Serbian Judges and the International Commission of Jurists, have an important role in protecting the rights of women. Radmila explained that this can be done through promoting international standards, ensuring that victims are made visible and ensuring that States understand their responsibilities and obligations.
Judicial education on gender-based violence is important, not just in countries undergoing transitional periods, but for all countries where regional and/or international standards have been developed.
Radmila advised anyone interested in defending women’s rights that this work can be done from any position or microsystem that an individual or group is operating in, providing they take the time to educate themselves and build awareness. What is important is that as many people as possible come together to promote and protect women’s rights. Progress can be made, even if this is little by little.
“Sometimes you think you are doing little and you feel hopeless”, said Radmila, “but then I always say if you put a little seed somewhere then it will grow, after you leave, in one year, two years it’s always worth it.”
Watch the video interview:
The series of profiles introducing the work of ICJ Commissioners and Honorary Members on women’s rights was launched on 25 November 2016 to coincide with the International Day to Eliminate Violence against Women and the first day of the 16 Days of Activism Against Gender-Based Violence Campaign.